Yoga
What is Yoga?
Science of unification of consciousness and nature
“The word yoga may fill the mind with images of mystical states of human experience. Is it meditation, prayer, physical exercise, or all? What exactly yoga is all about? For an all-round understanding let us explore the definition, history, benefits and variety of styles and schools of yoga in past and present”
The term yoga is derived from the Sanskrit root YUJ meaning to join or to unite. The practice of yoga leads to the union of individual consciousness with universal consciousness, indicating a perfect harmony between the mind and body, man, and nature.
Connecting Man and Nature
Nature consists of panchamahabhuta, many ancient scriptures mention that human body also consists of the panchamahabhuta. The panchamahabhutas are fire, water, earth, space & air. Accordingly in our human body comprises of fire, water, earth, space and air.


Brief History of Yoga
The yogic era is tentatively classified into four periods, (pre-Vedic period – 2700 BC; classical period – between 500 BC to 800 AD; post classical period – between 800 to 1700 AD; modern period – between 1700 to 1900 AD). From this we can say yoga modified or developed or grown-up in such a way along with our human evolution.
The yogic era is tentatively classified into four periods, (pre-Vedic period – 2700 BC; classical period – between 500 BC to 800 AD; post classical period – between 800 to 1700 AD; modern period – between 1700 to 1900 AD). From this we can say yoga modified or developed or grown-up in such a way along with our human evolution.


Diversity of styles and schools
Technically, yoga is classified as many variants such as, Jnana Yoga, Bhakti Yoga, Karma Yoga, Dhyana yoga, Patanjali yoga, Kundalini yoga, Hatha Yoga, Mantra Yoga, Laya Yoga, Raja Yoga, Jain Yoga, Buddha Yoga etc.
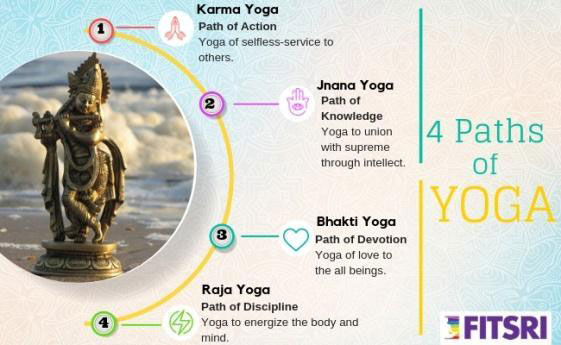
Belief of yoga in human nature
The ancient sages, philosophers and the traditional practitioners ‘strongly believed in holistic approach of yoga which brings harmony in all areas of life. It is thus, known for disease prevention, promotion of health and management of many lifestyles related disorders.
Result based life
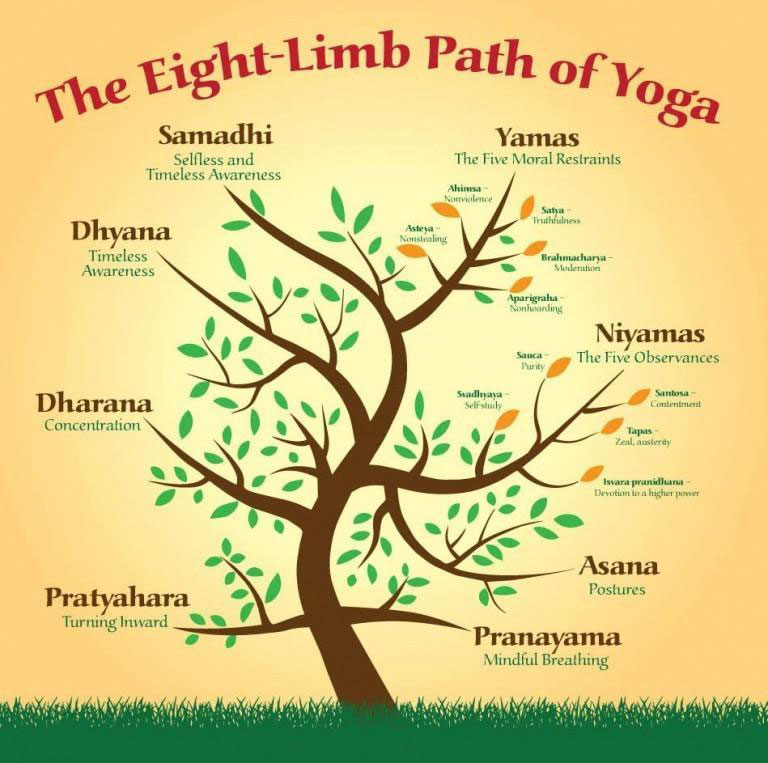
Result based working world of the modern times needs result by research. Satisfying these criteria, yoga science and research prove that yoga brings harmony between mind and body. Worldwide the word yoga is acceptable as a physical and mental health practice by following the great principle – Ashtanga Yoga which contains 8 parts viz.
Yama – universal ethical principles
Niyama – individual self-restraint
Asana – physical possess
Pranayama – breath work
Pratyahara – quitting the senses
Dharana – concentration
Dhyana – meditation
Samadhi – emancipation.
Belief and Truth
The recent evidence suggests that yoga exerts its therapeutic benefits by turning off Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis and Sympathetic Nervous System (Allostatic load) and it corrects under activity of parasympathetic nervous system & gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) system.
Yoga in Bachelor of Naturopathy and Yoga (BNYS)
By these concepts, yoga is added in our Indian system of medicine to treat a person as a whole and not only the external condition. Naturopathy medicine also clearly explains these.

